Experiential Learning activities are processes of teaching children by letting them solve real-world situations and absorb their reflections naturally. This leads to faster cognitive development and imprints those experiences on their subconscious mind forever.
Drawing a picture or making a toy with clay involves more senses than conventional methodology and allows students to discover new insights among themselves. Undoubtedly, the overall holistic development of a child can be achieved by framing theoretical knowledge into a practical skill set and therefore National Education Policy (NEP 2020) emphasizes more on experiential learning activities.
Laboratory experiments, field trips, projects, and artistic performances nurture the motivation, creativity, and critical thinking of students through practical exposure. Moreover, it deepens their understanding of the subject matter and its relevance to their lives which serves the greater purpose of life.
The concept of Experiential Learning Activities pedagogy was made popular by education theorist “David A. Kolb”, based on the idea that learning is a process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience.
Why are we studying Experiential Learning Pedagogy?
This topic is becoming the latest trend and therefore requires more exposure for the aspirants who are appearing in various Government exams, especially in EMRS, UGC NET, CTET, DSSSB, and various other educational fields. It is crucial to pay attention to this topic during preparation to maximize your chances of scoring well in the examination.
What are Experiential Learning Activities?
Experiential Learning Activities are referred to as learning through action, learning by doing, and learning through experience. It is a process through which students develop knowledge, skills, and values from direct experiences outside a traditional academic setting like internships, service learning, undergraduate research, study abroad, and other creative and professional work experiences.
Objectives and Principles of Experiential Learning:

- Affects the learner’s cognitive structures, attitudes, values, perceptions, and behavioral patterns.
- Experiences are designed to evoke decision-making, initiative, relationship-building, and accountability in learners.
- Learners accept new systems of action, thought, attitude, and behavior patterns when they accept membership in a new group.
- Provide learners with practical experience and applications of knowledge for better understanding.
- Experiential learning Activities foster an interest and connection to lifelong learning.
- Develops critical and abstract thinking skills for better problem-solving and relationship-building for the learners.
Check this out!
😜Guiding India’s Educational Renaissance with NCrF: The Dawn of a New Era: National Curriculum Framework 2023 (NCF 2023)
Importance of Experiential Learning:
- Makes learning relatable to learners: Learners build on what they already know and are provided with opportunities to connect new and existing concepts.
- Increases learning effectiveness: Learners engage in critical thinking, acquire problem-solving skills, and engage in decision-making.
- Link theories to practice: Learners have the chance to engage in the experience and practice what they have learned, see the application of the theoretical concepts in practice, process that application and make generalizations.
- Increase learner’s engagement: By encouraging collaboration and scaffolding between learners.
- Assists in memory retention: By building strong relationships between feelings and the thinking process. Learners can learn successfully when the information is associated with values and feelings.
- Leads to the development of skills for lifelong learning: By assisting in the acquisition of essential skills and encouraging learners to reflect, conceptualize, and plan for the next steps.
Experiential Activity Based Pedagogy in Teaching:
- Primary role of instructors is to identify a situation that challenges students through problem-solving, cooperation, collaboration, self-discovery, and self-reflection.
- At the same time decide what students should learn or gain from the learning experience.
- Adequate guidance and support must be exercised with proper collaboration and communication.
- Experiential learning Activities in pedagogy involve Plan-Prepare-Facilitate-Evaluate.
Check this out!
😜Decoding the Vision of Foundational Literacy and Numeracy: FLN Mission 2022: Unlock the Potential of Learner
Types of Experiential Learning :
| Types of Experiential Learning Activities & Pedagogy in Teaching | |
| Teaching learning practices | • Internship activities. • Investigate experiments. • Inquiring, investigating, and presenting information |
| Learning competencies | • Educational field hours. • Self responsibility & simulation. • Self-disciplined, reflection & direction. |
| Learning Environment | • Transforming classroom practices. • Resolution of conflicts & Information seeking. • Teamwork & collaboration. • Research & Scholarship. |
Kolb Experiential Learning Model:
Kolb argues that our educational experiences shape our learning styles and we should not be surprised to find relations between specialization and learning styles. The Experiential Learning Activities theory proposed by Kolb takes a more holistic approach and emphasizes how experiences, including cognition, environmental factors, and emotions, influence the learning process.
Kolb’s learning cycle stages:
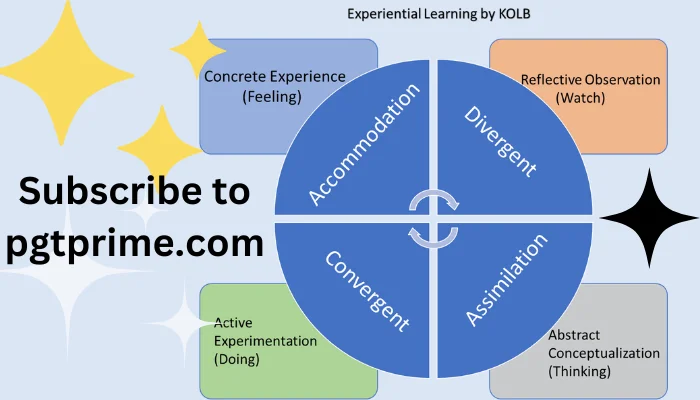
- Concrete experience (CE) » must do it yourself for learning to occur. Learners need to actively participate in the experience by feeling it with all five senses.
- Reflective observation (RO)» Taking a step back from doing to reflect and review. The learner must reflect upon the present situation by connecting it to his past experiences.
- Abstract conceptualization (AC) » Here you fit what you have just learned into everything you already know. The learner creates theories to explain his experiences. In this stage, the learner gathers and analyzes the information and draws conclusions.
- Active experimentation (AE) » This happens when you consider how you will put what you have learned into practice.
Kolb’s learning styles:
There are four learning styles based on the four stages of the Experiential Learning Activities cycle. These are:
- Converging style (Abstract, Active) » It involves doing and thinking process. The individual enjoys ideas and theory and tries to solve the problem practically.
- Diverging style (Concrete, Reflective) » It involves feeling and watching the process. Here an Individual prefers to watch than do.
- Assimilating style (Abstract, Reflective) » It involves watching and thinking process. An Individual enjoys ideas but is less interested in people and practical application or work. This kind of learner pulls many different observations and thoughts into an integrated whole.
- Accommodating style (Concrete, Active) » It involves doing and feeling process. An Individual prefers learning by doing. Students with this learning style use trial & error rather than thought and reflection.
Kolb’s learning cycle consists of four stages of action that have to take place for effective learning such as :
| 1. Feeling | 2. Observing | 3. Thinking | 4. Doing |
The model also describes different learning styles, acknowledging that as unique individuals, people prefer to learn in different ways.
Check this out!
😜All you need to know: ECCE (2024): The Best Power of Play in PreSchool
Experiential Learning Activities Examples:

| Learning to ride a bicycle: Experiential Learning Activities Examples | |
| Reflective observation | Thinking about riding & watching other persons riding a bicycle. |
| Abstract conceptualization | Understanding the theory & having a clear grasp of the riding concept. |
| Concrete experience | Receiving practical tips & techniques from a bicycle expert. |
| Active experimentation | Leaping on the bicycle and having a go at it. |
Experiential Learning in NEP 2020
Experiential Learning Activities plays a significant aspect of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. It emphasizes the importance of hands-on learning, arts-integrated and sports-integrated education, and story-telling-based pedagogy, among others, as standard pedagogy within each subject. This approach is designed to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skills among learners.
Experiential Learning Activities in NEP 2020-Pedagogy for Different Stages:
| Stage | Year | Age |
| Foundational Stage | 3 years 2 years | Age: 3 – 6 Age: 6 – 8 |
| Class Activities in the Secondary Stage • Anganwadi / PreSchool / BalVatika strengthened in terms of pedagogical strategies like playway, and activity field tours. • Activity-based learning, e.g: both indoor & outdoor play, puzzles, drawings, painting & crafts. | ||
| Preparatory Stage | 3 years | Age: 8 – 11 |
| Class Activities in the Preparatory Stage • pedagogical style of the foundational stage-learning opportunities to be built on the play discovery and activity-based drills, collaborative, and exploratory activities. • More interactive teaching-learning promotes exploratory activities, discussions, and questioning. | ||
| Middle Stage | 3 years | Age: 11 – 14 |
| Class Activities in Middle Stage • Integrated, cross-curricular approach. • Projects are to be done as a joyful activity. • Every student takes a fun course during Grade 6 that gives hands-on experience such as vocational crafts, carpentry, electric work, metal work, gardening, pottery making, etc. | ||
| Secondary Stage | 4 years | Age: 14 – 18 |
| Class Activities in the Secondary Stage • Teaching and learning will be conducted in a more interactive manner – encouraging questions, dialogue with fun, collaborative, and exploratory activities. • Arts-integrated and sports-integrated education, story-telling & lecture-based pedagogy. | ||
Check this out!
😜baseline assessment to propel NIPUN Bharat Mission: NIPUN Bharat Mission (2024): An Amazing Initiative in Education
How to Implement Experiential Learning:
Experiential Learning policy and framework in NCF:
A curriculum framework consists of a clear and implementable policy on how the growth and progress of education is envisaged with the help of various tools like syllabi, textbooks, pedagogy, extra-curricular activities, etc. NCF 2005, has put greater emphasis on designing task-based learning experiences that challenge students thinking and encourage independent thought and action.
State Govt’s initiatives for promoting Experiential Learning Activities:
- Uttar Pradesh– To improve children’s English, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (सर्व शिक्षा अभियान), UP supported by UNICEF, has initiated the program “Aao Angrezi Seekhen” (आओ अंग्रेजी सीखें). 15-minute bilingual interactive series designed in entertainment education format, which relies on local language support for learning English and is structured as a dramatized series in which young Hindi-speaking children learn English from an older English Speaker.
- Tamilnadu– Providing DVDs to schools which include poems from std 1 to 5. Each poem comes alive on the screen with the joyful expression of young children and provides an opportunity for fun-filled learning in primary schools.
- Chhattisgarh– Government collaborated with SAMPARK FOUNDATION. The Foundation helped develop maths and English kits for the school. MATH KIT contains a box with colorful materials like number lines, play money, numbers, and shapes. ENGLISH KIT comes with battery operated audio device to play the role of teacher effectively.
Classroom experiential learning
CBSE Initiatives on Experiential Learning Activities:
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has taken several initiatives to implement experiential learning in its affiliated schools.

- Revamped Affiliation bylaws with a focus on outcome-based education.
- The foundation of all qualitative improvements.
- Introduction of two-level mathematics at the secondary level.
- Adopting learning outcome-based education.
- Focus on education that imparts competencies to students.
- Strengthening assessment and evaluation practices.
- Integrating art with education.
- Focus on experiential and joyful learning.
- Reserving one period per day for sports and outdoor activities becomes mandatory at all levels.
- Formation of a cluster of schools into hubs of learning.
- Collaboration among affiliated schools for self-improvement and quality enhancement.
Check this out!
😜Governance and Capacity Building of Teachers for Quality Education: Embrace the change with NEP 2020 highlights
Scope of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning Activities are a powerful and effective approach to education that has a broad scope.
- School campus or a boarding component to campus life, here, students are responsible for some aspects of their daily life such as cleaning, time management, and study.
- Mock trials or debates should be organized.
- Organizing business internships.
- Undertaking drills to develop specific physical skills.
- Community service opportunities, to support disadvantaged communities.
- Study tours to international universities where students experience on-campus life and undertake undergraduate study.
- Simulations, such as in a business studies class examining the factors behind stock market fluctuations.
Conclusion on Experiential Learning Activities:
Learning is not imposed but implied when done through experience. When learners learn by actively involving and engaging with real-world experience, learning is to happen. Learners themselves direct their learning experiences and make meaningful connections based on their prior knowledge and past experiences.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS: On Experiential Learning Activities
Q: What are the experiential learning Activities?
A: Problem-solving through gamification and Simulations, such as in a business studies class examining the factors behind stock market fluctuations, Mock trials or debates should be organized, as case studies and role-play.
Q: What is the experiential learning Activities approach to pedagogy in NEP 2020?
A: The New Education Policy focuses on all essential aspects of education Learners have the chance to engage in the experience and practice what they have learned, see the application of the theoretical concepts in practice, process that application and make generalizations
Q: Is experiential learning a pedagogy?
A: The way of teaching students, whether it is the theory or practice of educating comes under pedagogy, here experiential learning itself means learning from experience or learning by doing.
Q: What are the features of experiential learning?
- Focus on education that imparts competencies to students.
- Strengthening assessment and evaluation practices.
- Integrating art with education.
- Focus on experiential and joyful learning.
Please let us know through the comment section if you want any topic to be discussed in this blog. We will try to provide an article on that subject as early as possible.
Please leave your valuable comment in the comment box! Your comments are valuable to us.












Very nice and informative article..